Introduction
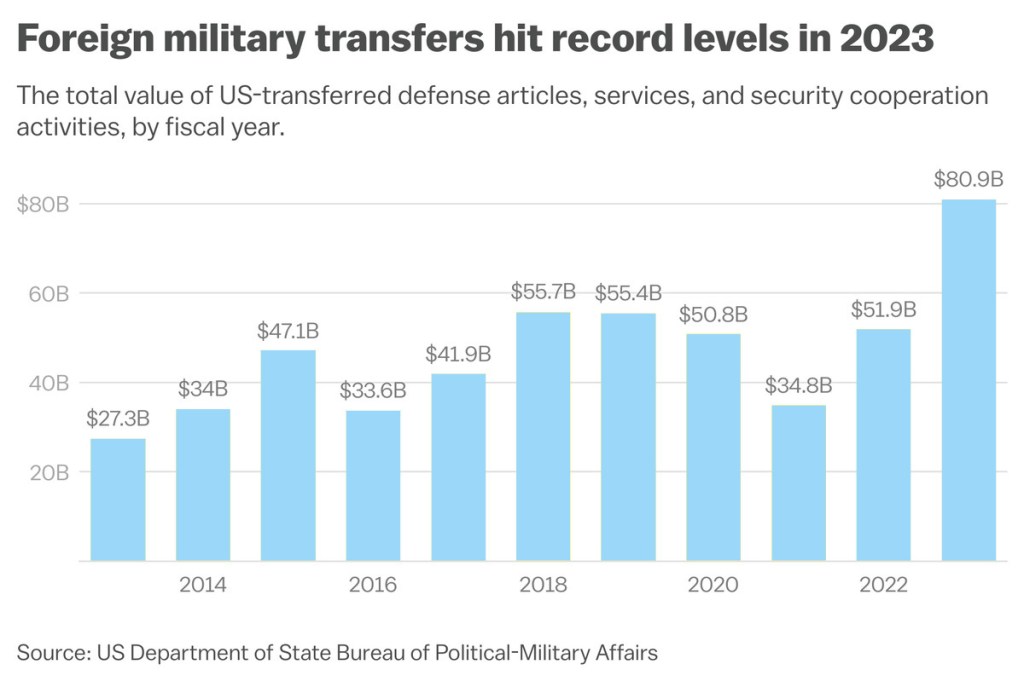
Foreign Military Sales (FMS) have undergone a remarkable evolution in recent years, driven by a complex interplay of geopolitical dynamics, technological advancements, and shifting alliances. As nation states seek to bolster their defense capabilities amidst a backdrop of global uncertainty, the FMS market has emerged as a critical avenue for the exchange of cutting-edge military technology and equipment, and ensuring the interoperability of allied forces. Over the past year, we have witnessed a huge surge in FMS transactions. In 2023, US FMS deals ballooned to $80.9 billion, and racked up a 55 percent hike in sales and deliveries to foreign countries over the previous year. That’s some serious growth, prompting both Congress and weapon system manufacturers to take notice.
Geopolitical Drivers of FMS Growth
One of the primary catalysts behind the growth of FMS has been the ever-changing geopolitical landscape. Tensions and regional conflicts have spurred nations to strengthen their military capabilities, leading to an increased demand for advanced weaponry and defense systems. From the Indo-Pacific region to Ukraine, the Middle East and beyond, nations are navigating complex security challenges, and pivoting to an era of great power competition characterized by an anti-access area denial (A2AD) highly contested battlespace, and the need for a primarily maritime strategy. Strategic alliances and partnerships have played a crucial role in shaping FMS trends, with countries seeking to forge closer ties with NATO & key allies to enhance their defense capabilities and deter potential adversaries. Escalating tensions in regions such as the South China Sea, the Korean Peninsula, and the Middle East have led to a heightened demand for military hardware and technology. Moreover, the evolving threat landscape, including the proliferation of non-state actors and the rise of cyber warfare has underscored the importance of staying ahead. As a result, countries have turned to FMS to acquire the latest defense systems and maintain a competitive edge in an increasingly volatile world.
Examination of Key Alliances and Partnerships
Strategic alliances and partnerships have emerged as key drivers of FMS growth, as countries seek to leverage collective security arrangements to address common threats and challenges. The United States, in particular, has deepened its defense ties with key allies and partners around the world, facilitating the transfer of advanced military technology through FMS channels. NATO member states, for instance, have increasingly relied on FMS to enhance interoperability and collective defense capabilities in the face of evolving security threats. Similarly, regional security alliances such as AUKUS have bolstered defense cooperation among like-minded nations, fostering a conducive environment for FMS transactions.
Impact of Technological Advancements on FMS
The rapid pace of technological innovation has revolutionized the defense industry and fundamentally transformed the nature of foreign military sales. Over the past five years, breakthroughs in areas such as artificial intelligence, unmanned systems, cyber defense, and space capabilities have reshaped the strategic landscape. As adversaries seek to exploit emerging technologies for strategic advantage, countries are increasingly turning to FMS to acquire the latest defense systems and maintain technological superiority. Moreover, the convergence of civilian and military technologies has blurred traditional boundaries, opening up new avenues for collaboration and innovation in the defense sector.

“The mission of the Defense Security Cooperation Agency (DSCA) is wide-ranging, encompassing Defense Trade and Arms Transfers, Institutional Capacity Building, International Military Training and Education, Humanitarian Assistance, and Security Cooperation Workforce Development. Since its inception in 1971, DSCA has been relied upon to lead the U.S. Security Cooperation enterprise to help solve complex U.S. defense and foreign policy challenges.” Credit: DSCA
Exploration of Emerging Defense Technologies in FMS
The proliferation of emerging defense technologies has fueled a surge in FMS transactions, as countries strive to modernize their armed forces and address evolving security threats. From next-generation fighter jets and unmanned aerial vehicles to advanced missile defense systems and cyber warfare capabilities, nations are actively seeking to enhance their military capabilities through the acquisition of state-of-the-art technology. Moreover, the growing importance of dual-use technologies has further expanded the scope of FMS, as countries look to leverage civilian innovations for military applications. As a result, defense contractors and technology companies are increasingly competing to meet the growing demand for advanced military hardware and software in the global marketplace.
Major FMS Deals in the Last 18 Months:

NETHERLANDS: $908 million for 1058 JASSM-ER and Hellfire missiles

TURKEY: $23 billion for F-16 aircraft and munitions

GREECE: $8.6 billion for F-35 aircraft and munitions

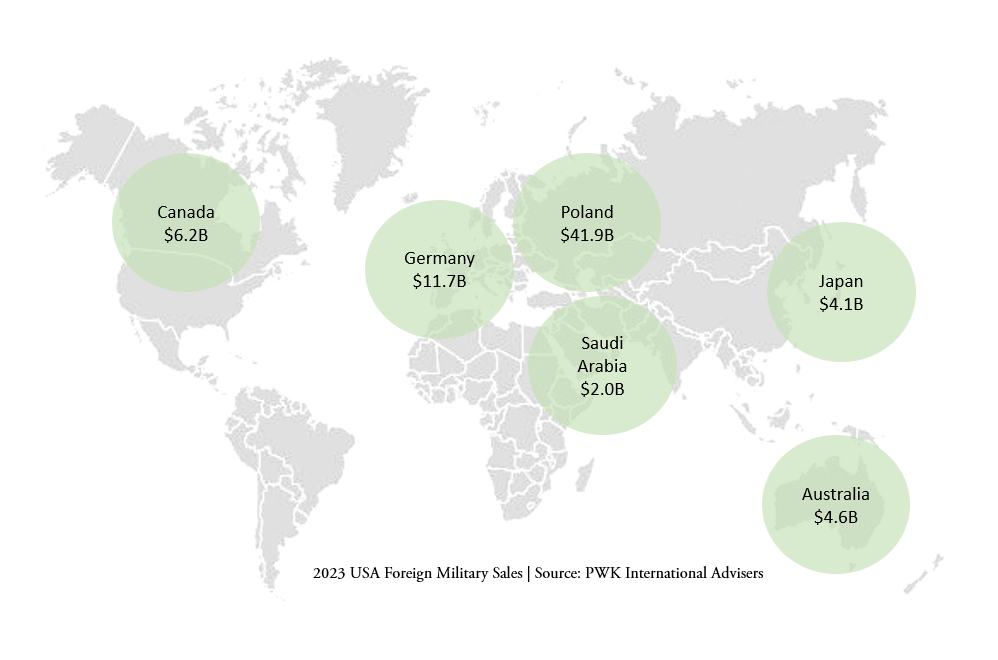
POLAND: $12 billion for 96 AH-64E Apache helicopters

POLAND: $10 billion for High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS)

GERMANY: $8.5 billion worth of CH-47F Chinook helicopters
Challenges and Opportunities in Technology Transfer
While technological advancements have unlocked new opportunities for defense cooperation and innovation, they have also created significant challenges in terms of technology transfer and export control. The increasing complexity and sensitivity of advanced military technology have raised concerns about the risk of proliferation and unauthorized use by adversaries. Consequently, countries must navigate a complex regulatory environment governing technology transfer and export licensing to ensure responsible and secure transfer of defense technology through FMS channels. Additionally, concerns about intellectual property rights, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and supply chain integrity have further complicated the technology transfer process, necessitating enhanced cooperation and coordination among stakeholders to mitigate risks and safeguard national security interests.

“The Defense Innovation Accelerator for the North Atlantic (DIANA) initiative serves as the innovation accelerator for NATO and will engage entrepreneurs, experts, mentors, and investors across the Alliance of 31 member nations to provide startups with access to subject matter expertise, testing environments, acquisition best practices, grant funding, and business development resources.”
Credit: NATO DIANA
Overview of Leading US Manufacturers and Technology Companies
The United States dominates the global FMS market, with its defense industry comprising a diverse array of manufacturers and technology companies at the forefront of innovation and production. Companies such as Lockheed Martin, Boeing, Raytheon Technologies, Northrop Grumman, and General Dynamics are among the key players driving FMS growth, leveraging their expertise and capabilities to meet the evolving defense needs of partner nations. These industry giants offer a wide range of advanced military hardware, including aircraft, missiles, naval vessels, cybersecurity solutions, and intelligence systems, making them indispensable partners for countries seeking to bolster their defense capabilities.
Analysis of Their Role in Driving FMS Growth
US manufacturers and technology companies play a pivotal role in driving FMS growth by providing cutting-edge military technology and equipment to allied and partner nations worldwide. Through strategic partnerships and collaborative ventures, these companies facilitate the transfer of defense systems and capabilities, strengthening the security posture of partner nations and fostering interoperability with US forces. Moreover, their ability to deliver integrated solutions tailored to the specific needs of customers enhances the effectiveness and efficiency of FMS transactions, enabling partner nations to address emerging threats and challenges more effectively.
Innovation and Competitive Advantage
Innovation lies at the heart of the competitive advantage enjoyed by US manufacturers and technology companies in the global FMS market. By investing heavily in research and development, these industry leaders continually push the boundaries of technological innovation, introducing groundbreaking solutions that shape the future of defense technology. From advanced stealth aircraft and precision-guided munitions to cutting-edge cyber and space capabilities, US companies remain at the forefront of innovation, driving the evolution of FMS and maintaining their position as preferred suppliers for partner nations seeking the most advanced military technology available.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite their dominant position in the FMS market, US manufacturers and technology companies face a myriad of challenges ranging from regulatory constraints and export controls to geopolitical instability and competition from foreign rivals. Navigating the complex regulatory landscape governing FMS transactions requires meticulous compliance with export control regulations and licensing requirements, which can pose logistical and administrative hurdles for companies seeking to export sensitive military technology. Moreover, geopolitical tensions and shifting alliances may impact market access and export opportunities, necessitating agile strategies and risk management measures to adapt to changing geopolitical dynamics. Nonetheless, the growing demand for advanced military technology presents significant opportunities for US companies to expand their global footprint and forge new partnerships, driving continued growth and innovation in the FMS market.
Exploring New Markets and Regions
Over the past five years, the FMS market has witnessed a notable expansion into new geographic regions and emerging markets, reflecting shifting geopolitical dynamics and evolving defense priorities. Traditionally, FMS transactions have been concentrated among longstanding allies and strategic partners of the United States. However, increasing global instability and the proliferation of security threats have prompted a broader array of nations to seek access to advanced military technology through FMS channels. As a result, countries in regions such as Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Africa are increasingly engaging in FMS transactions to modernize their armed forces and address emerging security challenges.
Diversification Strategies of US Companies
US manufacturers and technology companies are actively pursuing diversification strategies to capitalize on the expanding FMS market and mitigate risks associated with market volatility and geopolitical uncertainties. By diversifying their product offerings and targeting new customer segments, these companies aim to reduce their dependence on traditional markets and broaden their revenue streams. Moreover, strategic partnerships and joint ventures with foreign counterparts enable US companies to gain access to new markets and enhance their competitiveness in the global FMS arena. By leveraging their technological expertise and production capabilities, US companies can position themselves as preferred suppliers for a wide range of defense requirements, thereby maximizing opportunities for growth and expansion.

“Are we going to wait for the Pentagon for every dollar of revenue?”
Excerpt from the author in a conversation with managers about portfolio diversification at a major technology company. May 2022
Rise of Non-Traditional Suppliers
In addition to established players in the FMS market, non-traditional suppliers are emerging as significant contributors to the global arms trade, offering alternative sources of military technology and equipment to countries seeking to diversify their procurement options. Nations such as Israel, Turkey, Russia, China, and European countries have expanded their presence in the FMS market, leveraging their indigenous defense industries and geopolitical influence to forge strategic partnerships and secure lucrative contracts. This trend has led to increased competition and greater choice for buyers, as they evaluate a wider range of suppliers and technologies to meet their defense needs. Consequently, US companies face intensifying competition in the FMS market, prompting them to innovate and differentiate their offerings to maintain their competitive edge and retain market share.
Implications for Global Security and Stability
The expansion and diversification of the FMS market have significant implications for global security and stability, as countries seek to acquire advanced military capabilities to bolster their defense posture and assert their influence on the international stage. While FMS transactions can enhance the security capabilities of partner nations and promote interoperability among allied forces, they also raise concerns about arms proliferation, regional arms races, and destabilizing conflicts. Therefore, it is essential for stakeholders to prioritize responsible arms transfer practices, adhere to international arms control agreements, and promote transparency and accountability in FMS transactions to mitigate risks and safeguard regional and global security.
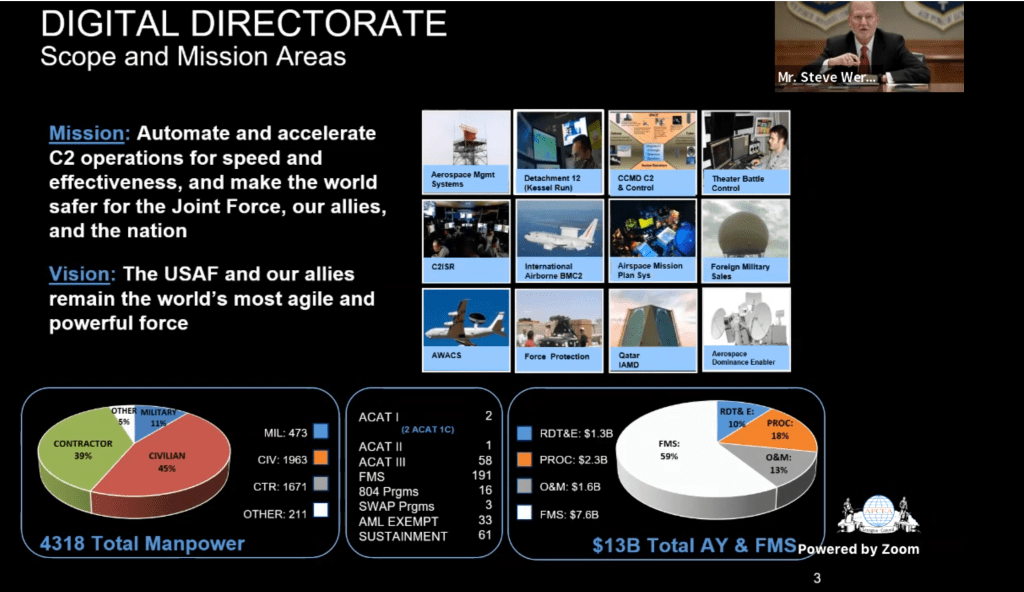
CHART CAPTION: The 17 division strong Program Executive Office Digital (a.k.a. Battle Management) or PEO HB Digital based out of Hanscom AFB in Lincoln MA. provides acquisition execution of a thirteen (13) billion dollar budget for delivering the war fighters edge in the air, in outer space, and in cyberspace. As part of the 16,800 man strong Air Force Life Cycle Management Center, the group is responsible for cradle to grave of all Air Force weapon systems. Comprised of a mix of uniformed military, high ranking federal employees, and a large number of embedded contractors, the 4,300 person group is organized and supported by test squadrons, applied research groups, proto-type engineering teams, multiple software factories, Federally Funded Research & Development Centers (i.e. MIT Lincoln Laboratory, MITRE, Aerospace Corp, Draper Labs), the Air Force Research Lab, and also helps deliver a portfolio of forty two (42) primary enterprise business services for a user base of 627,000 personnel. The chart above illustrates how 59% of the organizations activities are devoted to their growing Foreign Military Sales business of 190 customers. PEO Digital is also the largest PEO in the AFLCMC.
Source & Credit: Wert, Mr. Steven, Senior Executive Service (SES) AFLCMC HB PEO Digital | AFCEA Horizons 2022
Complex Regulatory Frameworks
Navigating the regulatory landscape governing foreign military sales (FMS) presents a formidable challenge for governments, defense contractors, and technology companies alike. The FMS process involves adherence to a complex web of international treaties, export control regimes, and national regulations aimed at safeguarding sensitive military technology and preventing unauthorized proliferation. Export control regimes such as the Wassenaar Arrangement, the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR), and the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) impose strict controls on the export of defense articles and services, requiring exporters to obtain licenses and comply with stringent security protocols.
Policy Shifts and Their Impact
In recent years, policymakers have implemented a series of policy shifts and reforms aimed at streamlining the FMS process, promoting defense trade, and enhancing strategic cooperation with key allies and partners. Initiatives such as the Defense Export Control Reform (DECR) initiative in the United States seek to modernize export control regulations, simplify licensing procedures, and facilitate the transfer of less sensitive defense articles to trusted partners. Moreover, efforts to strengthen defense industrial cooperation and technology transfer agreements between allied nations have facilitated greater collaboration in defense research, development, and production, driving innovation and interoperability among allied forces.
Challenges in Technology Transfer
Technology transfer lies at the heart of foreign military sales, enabling recipient nations to acquire advanced military capabilities and enhance their defense posture. However, technology transfer poses significant challenges in terms of protecting sensitive intellectual property, safeguarding national security interests, and mitigating the risk of unauthorized proliferation. Exporters must strike a delicate balance between facilitating technology transfer to support the defense needs of partner nations and safeguarding proprietary information and critical technologies from falling into the wrong hands. As a result, technology transfer agreements often involve rigorous vetting processes, robust security measures, and ongoing monitoring to ensure compliance with export control regulations and mitigate risks associated with unauthorized use or diversion of sensitive military technology.

Assessment of Economic Benefits for US Manufacturers
Foreign military sales (FMS) represent a significant source of revenue and economic opportunity for US manufacturers and technology companies, driving growth, innovation, and job creation in the defense industry. The export of defense articles and services through FMS channels generates billions of dollars in revenue annually, supporting thousands of high-skilled jobs across the United States. Furthermore, FMS transactions contribute to economies of scale and production efficiencies, enabling manufacturers to leverage their production capacity and expertise to meet both domestic and international demand for advanced military technology. As a result, FMS serves as a vital lifeline for the US defense industry, sustaining its competitiveness and ensuring its continued leadership in the global arms trade.
Strategic Implications of FMS for US Foreign Policy
Beyond its economic benefits, foreign military sales play a crucial role in advancing US foreign policy objectives and strengthening strategic partnerships with key allies and partners around the world. By providing allies and partners with access to advanced military technology and equipment, the United States enhances their defense capabilities and promotes regional stability and security. FMS transactions serve as a tangible demonstration of US commitment to collective defense and deterrence, reassuring allies of America’s steadfast support in times of crisis. Moreover, FMS fosters interoperability and military cooperation among allied forces, enabling more effective joint operations and crisis response efforts in an increasingly complex and unpredictable security environment.
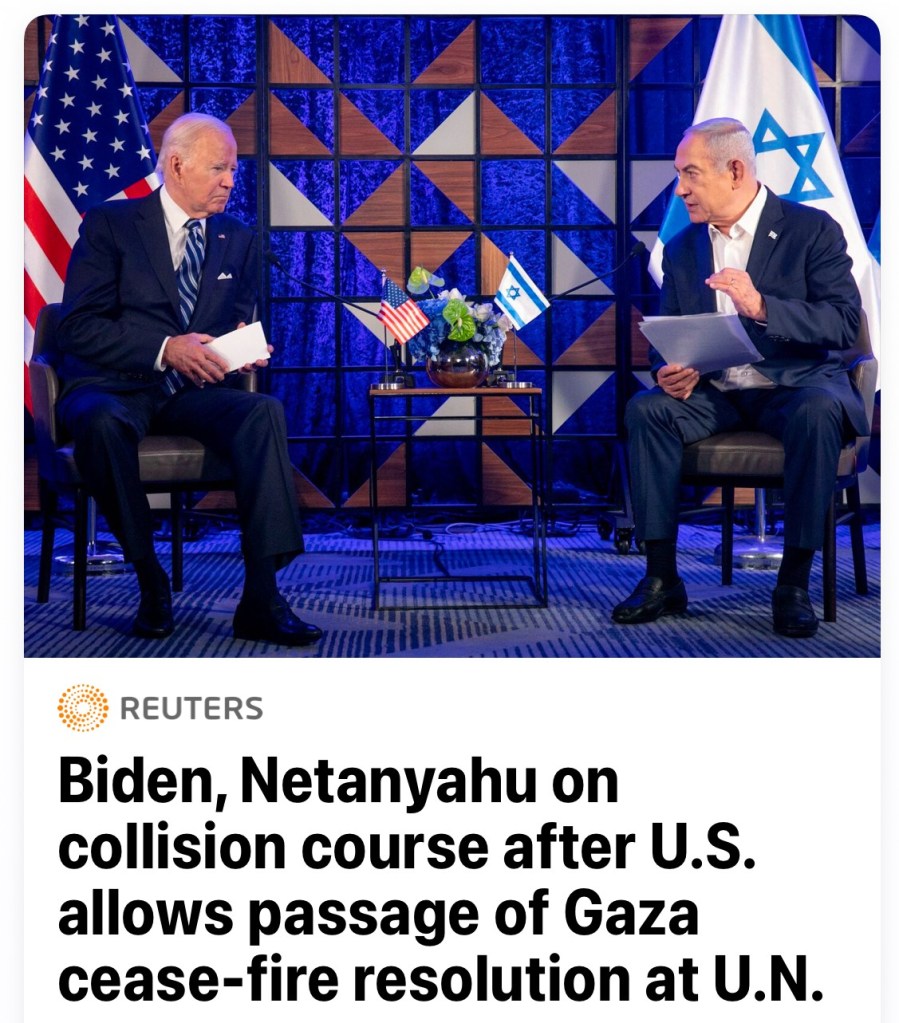
President Joe Biden, left meets with Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, right to discuss the ongoing conflict between Israel and Hamas in Gaza, and the planned invasion of Rafah. US – Israel relations have reached a new low due to the conflict.
Credit: Miriam Alster / Pool via REUTERS/File Photo
Promoting Regional Stability and Security
Foreign military sales have significant implications for regional stability and security, as they enable partner nations to address shared security challenges and maintain a credible deterrent against potential adversaries. By bolstering the defense capabilities of allies and partners, FMS transactions contribute to deterrence, reducing the likelihood of conflict and aggression in volatile regions. Moreover, by strengthening the military capabilities of partner nations, FMS helps build capacity for indigenous defense and security forces, enabling them to assume greater responsibility for regional security and contribute to collective security efforts. Additionally, FMS can promote stability by addressing asymmetric threats such as terrorism, piracy, and transnational crime, enhancing the resilience of partner nations and fostering a more secure and prosperous environment for economic development and growth.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the numerous benefits associated with foreign military sales, they also present challenges and considerations that must be carefully managed to ensure responsible and effective arms transfer practices. Concerns about human rights abuses, corruption, and diversion of military aid underscore the importance of robust due diligence and risk assessment processes to prevent the misuse of exported defense articles and services. Moreover, the potential for unintended consequences, such as arms races and regional instability, necessitates careful consideration of the strategic implications of FMS transactions and their long-term impact on global security dynamics. By addressing these challenges and considerations proactively, stakeholders can maximize the positive impact of foreign military sales on regional stability and security while mitigating potential risks and adverse consequences.

Predictions for the Future of FMS
Looking ahead, the future of foreign military sales (FMS) is poised for continued growth and evolution, driven by a combination of geopolitical shifts, technological advancements, and changing defense priorities. As geopolitical tensions persist and security threats become increasingly complex and multifaceted, nations are expected to prioritize the modernization and expansion of their defense capabilities, fueling demand for advanced military technology and equipment through FMS channels. Moreover, the growing interdependence and interconnectedness of global security challenges are likely to drive greater cooperation and collaboration among allied and partner nations, leading to increased demand for joint defense solutions and interoperable capabilities.
Emerging Technologies and Disruptive Innovations
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, autonomous systems, quantum computing, and directed energy weapons are expected to play a transformative role in shaping the future of FMS. As these technologies mature and become more accessible, nations will seek to leverage them to gain a strategic advantage and maintain military superiority in an increasingly contested and competitive environment. Consequently, defense contractors and technology companies will need to invest in research and development to stay at the forefront of innovation and meet the evolving defense needs of partner nations. Moreover, the convergence of civilian and military technologies is likely to blur traditional boundaries, opening up new opportunities for collaboration and partnership between defense and commercial sectors.
Policy and Regulatory Considerations
Policy and regulatory frameworks governing FMS will continue to evolve in response to changing geopolitical dynamics and emerging security challenges. Governments will need to strike a delicate balance between facilitating defense trade and technology transfer to support allied and partner nations while safeguarding national security interests and preventing the proliferation of sensitive military technology. Moreover, efforts to promote responsible arms transfer practices, enhance transparency and accountability, and strengthen international cooperation and coordination will be essential to mitigate risks and ensure the responsible use of exported defense articles and services.
Conclusion
Foreign military sales (FMS) have emerged as a critical instrument of international security cooperation, enabling nations to enhance their defense capabilities and address shared security challenges through the transfer of advanced military technology and equipment. Over the past five years, FMS has experienced significant growth and evolution, driven by geopolitical tensions, technological advancements, and changing defense priorities. Looking ahead, the future of FMS is characterized by continued expansion and innovation, with emerging technologies and disruptive innovations shaping the strategic landscape and driving demand for advanced defense solutions. However, as FMS transactions become increasingly complex and interconnected, policymakers, industry stakeholders, and international organizations must work together to address regulatory challenges, and promote responsible arms transfer practices.
About PWK International Advisers
PWK International provides national security consulting and advisory services to clients including hedge Funds, Financial Analysts, Investment Bankers, Entrepreneurs, Law Firms, Non-profits, Private Corporations, Technology Startups, Foreign Governments, Embassies & Defense Attaché’s, Humanitarian Aid organizations and more.
Services include telephone consultations, analytics & requirements, technology architectures, acquisition strategies, best practice blue prints and roadmaps, expert witness support, and more.
From cognitive partnerships, cyber security, data visualization and mission systems engineering, we bring insights from our direct experience with the U.S. Government and recommend bold plans that take calculated risks to deliver winning strategies in the national security and intelligence sector. PWK International – Your Mission, Assured. Learn More.